Evicting a tenant in Nebraska can take around 1 to 2 months, depending on the reason for the eviction. If tenants file an appeal, the process can take longer.
Grounds for an Eviction in Nebraska
In Nebraska, a landlord cannot legally evict a tenant without cause. Legal grounds to evict include:
- Not paying rent on time
- Staying after the lease ends
- Violating the terms of the lease
- Committing illegal activity.
Depending on the grounds for eviction, the landlord must give proper notice and provide the tenant a chance to cure the violation.
| Grounds | Notice Period | Curable? |
| Nonpayment of Rent | 7 Days | Yes |
| End of Lease or No Lease | 30 Days | No |
| Lease Violation | 30 Days | Yes |
| Repeat Lease Violation | 14 Days | No |
| Illegal Activity | 5 Days | No |
Nonpayment of Rent
In Nebraska, a landlord can evict a tenant for not paying rent on time. To do so, the landlord must first serve the tenant a 7 days’ notice to quit, which gives the tenant a chance to pay the balance due or move out.
Unless the lease states otherwise, rent is due at the beginning of each month and is considered late in Nebraska the day immediately after its due date. Nebraska landlords are not required to give tenants a rent payment grace period. However, if the lease or rental agreement allows for one, then the landlord must honor it.
If rent is due on September 1st, it will be considered late starting on September 2nd, unless the lease specifically states there is a grace period.
If the tenant does not pay the balance due or move out by the end of the notice period, the landlord can move forward and file an eviction lawsuit.
End of Lease or No Lease
In Nebraska, a landlord can evict a tenant who does not have a lease (“tenant at will”) or has a lease that has terminated and continues to remain on the premises (“holdover tenant”). To do so, the landlord must first terminate the tenancy by giving the tenant a proper 30-day notice to move out.
If the tenant does not move out by the end of the notice period, the landlord can move forward and file an eviction lawsuit.
Lease Violations
In Nebraska, a landlord can evict a tenant for violating the terms of their lease or not upholding their responsibilities under Nebraska landlord-tenant law. To do so, the landlord must first serve the tenant a 30 days’ notice to comply or vacate, which gives the tenant a chance to fix the issue within 14 days or move out within 30 days.
Examples of lease violations include:
- Failing to maintain the premises in a clean and sanitary manner
- Refusing to allow the landlord access to the rental unit
- Disturbing the peace and enjoyment of other persons
- Allowing unauthorized persons or pets on the premises
- Damaging electrical wiring in the rental unit
If the tenant does not fix the issue or move out by the end of the notice period, the landlord can move forward and file an eviction lawsuit.
Repeat Lease Violations
In Nebraska, a landlord can evict a tenant for repeating the same or a similar lease violation within a 6-month period. To do so, the landlord must first serve the tenant a 14 days’ notice to vacate.
The tenant does not have the chance to fix the issue and must move out within the 14-day period. If the tenant does not move out by the end of the notice period, the landlord can move forward and file an eviction lawsuit.
Illegal Activity
In Nebraska, a landlord can evict a tenant for committing illegal activity on the premises. To do so, the landlord must first serve the tenant a 5 days’ notice to vacate. The tenant does not have a chance to fix the violation and must move out within the 5-day period.
In Nebraska, illegal activity includes:
- Threatening physical assault or committing a physical assault
- Illegally threatening or using a firearm or other weapon
- Possessing or illegally selling controlled substances
- Engaging in any other activity that would harm the health and safety of other persons or the premises
- Committing any other activity that is prohibited by law
If the tenant does not move out by the end of the notice period, the landlord can move forward and file an eviction lawsuit.
Illegal Evictions in Nebraska
In Nebraska, there are a few different types of evictions that are illegal. If found liable, the landlord could be required to pay the tenant an amount equal to three month’s periodic rent and reasonable attorneys’ fees.
“Self-Help” Evictions
A landlord is not allowed to forcibly remove a tenant by:
- Changing the locks
- Shutting off utilities
- Removing tenant belongings
A tenant can only be legally removed with a court order obtained through the formal eviction process.
Retaliatory Evictions
It is illegal for a landlord to evict a tenant in response to exercising a legally protected right. These rights include:
- Complaining about a housing code to the landlord or any authority tasked to enforce the law
- Joining a tenant’s union or organization
- Filing a lawsuit against the landlord or testifying or participating in a lawsuit that involves the landlord
In Nebraska, evictions follow the same process:
- Landlord serves tenant with written notice of violations
- Landlord files complaint with court for unresolved issues
- Court holds hearing and issues judgment
- Writ of restitution is posted
- Possession of property is returned to landlord
Step 1: Landlord Serves Notice To Tenant
A landlord can begin the eviction process in Nebraska by serving the tenant with written notice. Nebraska landlords may deliver a written eviction notice by any method which results in actual notification of the tenant. In Nebraska, the following methods of notice have a presumption of legal validity:
- Hand delivery to the tenant
- Delivery by mail to the tenant’s address of record, or (if unknown) last place of residence
Notice is considered effective from when it comes to the other party’s attention, or reasonably should do so under the circumstances. Mailed notice extends the notice period by three (3) calendar days, to account for variable delivery times.
Landlords should always keep the original signed notice and declaration of service as proof of proper service if the case proceeds to court.
7-Day Notice To Quit
In Nebraska, if a tenant is late on paying rent (full or partial), the landlord can serve them a 7-Day Notice To Quit. This eviction notice gives the tenant 7 days to pay the balance due or move out.
30-Day Notice To Vacate
For a tenant with no lease or a month-to-month lease in Nebraska, the landlord can serve them a 30-Day Notice To Vacate to terminate the tenancy. This lease termination notice allows the tenant 30 days to move out.
For tenants that don’t pay monthly, the amount of notice differs:
| Rent Payment Frequency | Notice Amount |
|---|---|
| Week-to-Week | 7 Days |
| Month-to-Month | 30 Days |
30-Day Notice To Comply or Vacate
In Nebraska, if a tenant violates the terms of their lease or does not uphold their legal responsibilities, the landlord can serve them a 30-Day Notice To Comply or Vacate. This eviction notice gives the tenant 14 days to fix the issue or 30 calendar days to move out.
14-Day Notice To Vacate
In Nebraska, if a tenant repeats the same or a similar lease violation within a six-month period, the landlord can serve them a 14-Day Notice To Vacate. This eviction notice gives the tenant 14 days to move out without the chance to fix the issue.
5-Day Notice To Vacate
In Nebraska, if a tenant commits an illegal activity, the landlord can serve them a 5-Day Notice To Vacate. This eviction notice gives the tenant 5 days to move out without the chance to fix the issue.

Step 2: Landlord Files Lawsuit with Court
As the next step in the eviction process, Nebraska landlords must file a complaint in the appropriate court. In the state of Nebraska, this costs $85 in filing fees for eviction cases filed in District Court.
The summons and complaint may be served on the tenant by the sheriff or anyone else who isn’t a part of the case within3 days of the date the summons was issued by the court, through one of the following methods:
- Giving a copy to the tenant in person
- Leaving a copy at the tenant’s residence with someone of suitable age
- Mailing a copy via certified mail
- Using a designated delivery service to deliver a copy to the tenant
- Posting a copy at the rental unit AND mailing a copy via first class mail
It is important to note that posting a copy may only be done if all other service methods fail. The landlord shall file an affidavit noting the diligent efforts to serve the summons.

Step 3: Court Hearing and Judgment
The eviction hearing must be held 10-14 days after the summons is issued.
In Nebraska, landlords and tenants do not have the right to a jury trial, and the eviction hearing will be held before a judicial officer only. If the tenant fails to appear for the hearing, the judicial officer may issue a default ruling in favor of the landlord, meaning the tenant will have to move out.
If the judge rules in favor of the landlord, either through a default judgment or at an eviction hearing, a writ of restitution will be issued, and the eviction process will continue.
The eviction hearing must be held at least 10 days, but not more than 14 days, after the date the summons is issued by the court.
Step 4: Writ of Restitution Is Issued
The writ of restitution is the tenant’s final notice to leave the rental unit and gives them the opportunity to remove their belongings before a sheriff or constable returns to the property to forcibly remove them.
If the court has ruled in the landlord’s favor, the landlord will ask the court to issue a writ of restitution. Nebraska state law doesn’t specify how quickly this must be done after the judgment is issued in favor of the landlord.
The landlord must request the writ of restitution, but it can be issued the same day as the hearing.
Step 5: Possession of Property is Returned
A sheriff or constable must remove tenants from the rental unit within 10 days of the date the writ of restitution is issued by the court.
This could mean tenants have to move out the day the court hearing is held, depending on how quickly the landlord requests the writ of restitution.
The tenant has 10 days at the most once the writ of restitution has been issued to move out before a law enforcement officer is allowed to forcibly remove them from the property.
Nebraska Eviction Process Timeline
In Nebraska, an eviction can be completed in 1 to 2 months but can take longer depending on the reason for eviction, whether the eviction is contested, which days courts are (or aren’t) in session and other various possible delays.
Below are the parts of the Nebraska eviction process outside the control of landlords for cases that go uncontested.
| Step | Estimated Time |
|---|---|
| Initial Notice Period | 5-30 Calendar Days |
| Court Issuing/Serving Summons | 3 Business Days |
| Tenant Response Period | Not Required |
| Court Ruling | 10-14 Business Days |
| Court Serving Writ of Restitution | 1-3 Business Days |
| Final Notice Period | 1-10 Calendar Days |
Flowchart of Nebraska Eviction Process
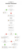
Nebraska Eviction Court Fees
The total cost of an eviction in Nebraska for all filing, court, and service fees varies heavily on the service fees. For cases filed in District Court, the average cost is $128. For cases filed in County Court, the average cost is $91.
| Fee | District | County |
| Initial Court Filing | $86 | $49 |
| Summons Service | ~$12+ | ~$12+ |
| Writ of Restitution Service | $12 | $12 |
| Writ of Restitution Execution | $18 | $18 |
| Notice of Appeal Filing (Optional) | $75 | $100 |
Sources
- 1 NE Rev Stat §76-1431 (2019)
-
(2) If rent is unpaid when due and the tenant fails to pay rent within seven calendar days after written notice by the landlord of nonpayment and his or her intention to terminate the rental agreement if the rent is not paid within that period of time, the landlord may terminate the rental agreement.
- 2 NE Rev Stat §76-1437 (2019)
-
(1) The landlord or the tenant may terminate a week-to-week tenancy by a written notice given to the other at least seven days prior to the termination date specified in the notice. (2) The landlord or the tenant may terminate a month-to-month tenancy by a written notice given to the other at least thirty days prior to the periodic rental date specified in the notice.
- 3 NE Rev Stat §76-1431 (2019)
-
(1) …if there is a noncompliance with section 76-1421 materially affecting health and safety or a material noncompliance by the tenant with the rental agreement or any separate agreement, the landlord may deliver a written notice to the tenant…that the rental agreement will terminate upon a date not less than thirty days after receipt of the notice if the breach is not remedied in fourteen days…
- 4 NE Rev Stat §76-1431 (2019)
-
(4) …after five days’ written notice of termination of the rental agreement and without the right of the tenant to cure the default, file suit …for recovery of possession …if the tenant… engages in any violent criminal activity on the premises, the illegal sale of any controlled substance on the premises, or any other activity that threatens the health or safety…
- 5 NE Rev Stat §76-1431 (2019)
-
(4)(a) Physical assault or the threat of physical assault; (b) illegal use of a firearm or other weapon or the threat of illegal use of a firearm or other weapon; (c) possession of a controlled substance…or (d) any other activity or threatened activity which would otherwise threaten the health or safety of any person or involving threatened, imminent, or actual damage to the property.
- 6 NE Rev Stat §76-1430 (2021)
-
If the landlord unlawfully removes or excludes the tenant from the premises or willfully and wrongfully diminishes services to the tenant by interrupting or causing the interruption of electric, gas, water or other essential service to the tenant, the tenant may recover possession or terminate the rental agreement and, in either case, recover an amount equal to three months’ periodic rent as liquidated damages, and a reasonable attorney’s fee. If the rental agreement is terminated the landlord shall return all prepaid rent and security recoverable under section 76-1416.
- 7 NE Rev Stat §76-1439 (2021)
-
(1) Except as provided in this section, a landlord may not retaliate by increasing rent or decreasing services or by bringing or threatening to bring an action for possession after:
(a) The tenant has complained to a government agency charged with responsibility for enforcement of a minimum building or housing code of a violation applicable to the premises materially affecting health and safety; or
(b) The tenant has organized or become a member of a tenants’ union or similar organization.
(2) If the landlord acts in violation of subsection (1), the tenant is entitled to the remedies provided in section 76-1430 and has a defense in action against him for possession. Nothing in this section shall be construed as prohibiting reasonable rent increases or changes in services notwithstanding the occurrence of acts specified in subsection (1).
(3) Notwithstanding subsections (1) and (2), a landlord may bring an action for possession if:
(a) The violation of the applicable minimum building or housing code was caused primarily by lack of reasonable care by the tenant or other person in his household or upon the premises with his consent;
(b) The tenant is in default in rent; or
(c) Compliance with the applicable minimum building or housing code requires alteration, remodeling, or demolition which would effectively deprive the tenant of use of the dwelling unit.
The maintenance of the action does not release the landlord from liability under subsection (2) of section 76-1425.
- 8 NE Rev Stat §25-506.01 (2019)
-
(1) Unless the plaintiff has elected certified mail service or designated delivery service, the summons shall be served by the sheriff… by a person authorized by section 25-507 or otherwise authorized by law, or by a person…not a party to the action specially appointed by the court for that purpose. (2) Certified mail service or designated delivery service shall be made by the plaintiff or plaintiff’s attorney.
- 9 NE Rev Stat §76-1442 (2019)
-
The summons may be served and returned as in other cases or by any person, except that the summons shall be served within three days, excluding nonjudicial days, from the date of issuance and shall be returnable within five days, excluding nonjudicial days, from the date of issuance.
- 10 NE Rev Stat §25-505.01 (2019)
-
(1)(a) … leaving the summons with the individual to be served; (b) … leaving the summons at the usual place of residence … with some person of suitable age and discretion residing therein; (c) Certified mail…(d) Designated delivery service …
- 11 NE Rev Stat §76-1442.01 (2019)
-
…service of a summons…may be made by leaving a copy of the summons at the defendant’s last-known address and mailing a copy by first-class mail…The plaintiff shall file an affidavit…showing that an attempt was made to serve the summons in the manner provided in sections 25-505.01 to 25-516.01, the reasons why such service was unsuccessful…
- 12 NE Rev Stat §76-1446 (2019)
-
Trial of the action for possession shall be held not less than ten nor more than fourteen days after the issuance of the summons. The action shall be tried by the court without a jury.
- 13 NE Rev Stat §76-1446 (2019)
-
…the court shall declare the forfeiture of the rental agreement, and shall, at the request of the plaintiff or his or her attorney, issue a writ of restitution, directing the constable or sheriff to restore possession of the premises to the plaintiff on a specified date not more than ten days after issuance of the writ of restitution.
- 14 Neb. Rev. Stat. § 76-1413
-
Source Link
(1) A person has notice of a fact if (a) he has actual knowledge of it, (b) he has received a notice or notification of it, or (c) from all facts and circumstances known to him at the time in question he has reason to know that it exists. A person knows or has knowledge of a fact if he has actual knowledge of it. (2) A person notifies or gives a notice or notification to another by taking steps reasonably calculated to inform the other in ordinary course whether or not the other actually comes to know of it. A person receives a notice or notification when (a) it comes to his attention, (b) in the case of the landlord, it is delivered at the place of business of the landlord through which the rental agreement was made or at any place held out by him as the place for receipt of the communication, or (c) in the case of the tenant, it is delivered in hand to the tenant or mailed to him at the place held out by him as the place for receipt of the communication, or in the absence of such designation, to his last-known place of residence. (3) Notice, knowledge or a notice or notification received by an organization is effective for a particular transaction from the time it is brought to the attention of the individual conducting that transaction, and in any event from the time it would have been brought to his attention if the organization had exercised reasonable diligence. - 15 Neb. Ct. R. Pldg. § 6-1106(e)
-
Additional Time After Service by Mail. Whenever a party has the right or is required to do some act or take some proceedings within a prescribed period after the service of a notice or other document upon the party and the notice or document is served under § 6-1105(b)(2)(B), three days shall be added to the prescribed period.
Source Link