Washington law defines many actions that landlords cannot do. Find out what’s allowed, when they’re allowed, and what the consequences for illegal landlord actions are.
1. Retaliate
Landlords in Washington cannot retaliate against tenants for exercising their rights under the law. A tenant’s legal rights may include reporting violations to a local health board or withholding rent because of a landlord’s failure to make necessary repairs.
Actions that may constitute retaliation include:
- Increasing rent
- Terminating a lease
- Evicting a tenant
- Decreasing services or access to amenities
Consequences for Landlords Who Retaliate
Landlords who retaliate are at risk of having the tenant terminate the lease and sue the landlord. If a court decides the landlord has retaliated against the tenant, the following penalties may be assessed:
- One month’s rent plus $500
- Reasonable costs to move to another place
- Attorney’s fees and costs
- Injunctive relief
When Can a Landlord Retaliate?
Under landlord-tenant law in Washington, there is never a time that a landlord can retaliate against a tenant for exercising their rights.
However, actions that may seem retaliatory can be legal if within the law. For instance, a landlord may increase the rent at the end of the lease term, and terminate a lease or evict a tenant for violating the terms of the agreement.
2. Discriminate
Under the Fair Housing Act, landlords cannot discriminate against a tenant based on protected characteristics such as race, color, national origin, religion, sex, familial status, or disability.
Discriminatory acts include:
- Harassing tenants
- Refusing to rent and making housing unavailable to a tenant
- Setting different terms and conditions for certain tenants
- Providing different services to certain tenants
A landlord does not provide reasonable accommodations to persons in wheelchairs such as ramps.
Consequences for Landlords Who Discriminate
Landlords who discriminate are at risk of having the tenant terminate the lease and sue the landlord. When suing the landlord, a tenant may either file a complaint with the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) or the federal court in the jurisdiction where the tenant resides.
If either HUD or a federal court decides the landlord has discriminated against the tenant, the tenant may be eligible for the following remedies:
- Compensation for actual damages
- Injunctive relief
- Equitable relief such as providing alternative housing
- Reasonable attorney’s fees
- Payment of civil penalties
When Can a Landlord Discriminate?
In Washington, a landlord can never discriminate against a tenant, except in one instance. The exception is known as the “Mrs. Murphy Exemption”.
The “Mrs. Murphy” exemption provides that if a dwelling has four or fewer rental units and the owner lives in one of those units, that owner is exempt from the Fair Housing Act. Therefore, a landlord would be able to discriminate against tenants.
There is a blanket ban on a landlord discriminating against the tenant because of race. No matter the Mrs. Murphy exemption, a landlord can never discriminate against a tenant because of race.
Furthermore, the exemption does not apply to rental advertisements. For example, the owner of the dwelling cannot be discriminatory in their advertisements by saying that people of a certain sexual orientation or race need not apply just because the dwelling itself is exempt from the Fair Housing Act.
3. Evict Without Cause
In Washington, landlords cannot evict a tenant or force them to vacate the rental premises without legal cause that a tenant violated the lease.
A landlord may have legal grounds for evicting a tenant if the tenant:
- Does not pay rent on time
- Stays after the lease ends
- Violates the lease terms
- Does not uphold legal responsibilities
Consequences for Landlords Who Evict Tenants Without Cause
Landlords who evict their tenants without legal cause will be liable to the tenant for certain damages. If a court finds the landlord evicted the tenant without cause, the landlord may be liable for:
- One month’s rent plus $500
- Reasonable costs to move to another place
- Attorney’s fees and costs
- Injunctive relief
Once a court finds there was no cause for eviction, tenants will be allowed to return into the leased premises.
Eviction Without Adequate Notice
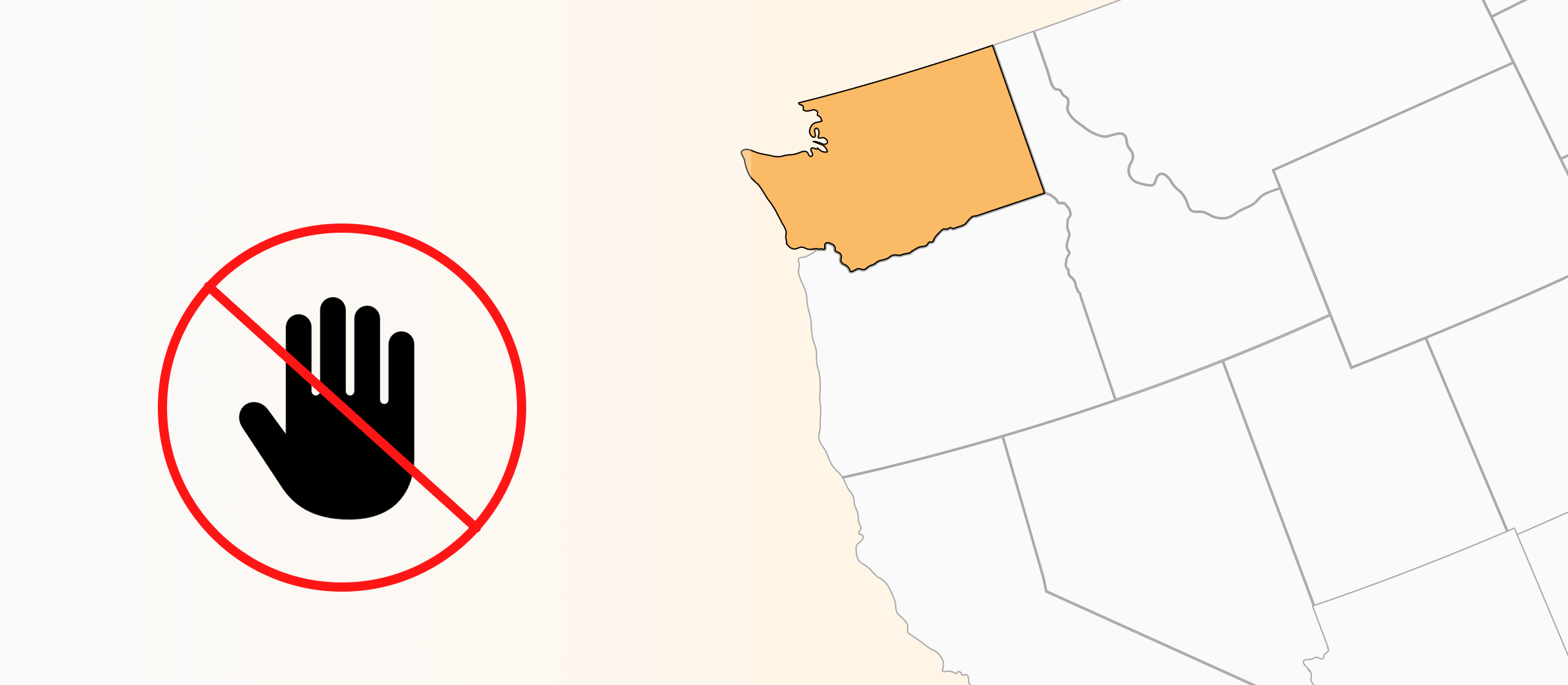
Washington landlords may not evict without adequate notice. Like some other states, Washington courts have held that many properties are federally entitled to a minimum 30 days of advance notice before a landlord can file for eviction. This applies to residential property covered by the federal Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act, even after the act’s other protections have expired.
Washington courts have conflicting standards on exactly when the 30-day requirement applies. CARES Act properties in Appellate Division I only require 30 days of notice for nonpayment of rent. Division II requires 30 days of notice for ALL CARES property evictions. Division III has not established a clear standard as of 2024, and requirements may differ by county.
This map shows which Washington counties are governed by which appellate division. When in doubt, a 30 day notice is always the legally safer option.
When Can a Landlord Evict a Tenant?
In Washington, a landlord cannot legally evict a tenant without cause. However, a landlord would be able to evict a tenant on legal grounds such as the tenant not paying rent on time, staying after the lease ends, violating lease terms or not upholding responsibilities under Washington law.
Eviction proceedings include:
- Written Notice To Vacate
- Filing of the Eviction Suit
- Judgment
- Appeal
- Writ of Possession
Ensure that the tenant has violated the lease terms prior to initiating an eviction lawsuit.
4. Increase Rent During the Lease Term
A landlord in Washington cannot raise the rent as often as they want nor increase it by an unreasonable amount during the life of the lease term. A rent increase will be illegal if it is done in any of three instances:
- Before the expiration of the current lease
- In a discriminatory way
- As an act of retaliation
Consequences for Landlords Who Raise Rent
Unless written into the lease, a landlord cannot increase rent prior to the end of the contract. When landlords do raise the rent for the aforementioned reasons, they will be in violation of the lease, and the tenant will be able to terminate the lease. Landlords may also be charged fines and penalties associated with increasing rent.
Before raising the rent, a landlord should ensure that it is done after the lease term has ended. If the proper procedure is outlined in the lease, those procedures should be followed.
When Can a Landlord Increase the Rent?
A landlord can increase rent at the end of any lease term. A lease is a legally binding contract, and the landlord must abide by the terms, including the set monthly rent. However, there are no control laws in Washington, so any time a lease expires, the landlord can raise the rent as much as they like and allow the tenant the chance to renew at the new rate.
If the lease is for two years, the landlord can only raise the rent every two years, but if it’s a month-to-month lease, they can raise it every 30 days if they so choose.
5. Withhold Security Deposits
In Washington, a landlord may not withhold the tenant’s security deposit for any disallowed reason.
For example, a landlord would be unable to withhold the security deposit for property damage incurred from normal wear and tear. Normal wear and tear is deterioration or damage that happens as a result of a tenant living in and using the rental unit in a reasonable manner.
Consequences for Landlords Who Withhold Security Deposits
A landlord who withholds a tenant’s security deposit will be responsible for repaying the tenant the whole security deposit amount. Furthermore, the landlord may also be on the hook for attorney’s fees and three times the amount of the security deposit.
When Can a Landlord Withhold a Tenant’s Security Deposit?
A landlord will be able to withhold a tenant’s security deposit for certain reasons. These reasons include:
- Damages incurred because of lease breaches
- Damages not resulting from ordinary use
- Unpaid monthly rent
- Unpaid utilities
- Cleaning fees for degradation not resulting from ordinary use
- Expenses incurred in securing a new tenant
- Lease cancellation fees
Landlords must provide an itemized list of any deductions made, within 30 days. Deductions must be justified by showing receipts, invoices, estimates, and similar documentation that a deduction reflects actual costs. A landlord cannot deduct for any item whose condition was not described in the required move-in checklist.
6. Violate the Covenant of Quiet Enjoyment
Landlords in Washington cannot violate the covenant of quiet enjoyment, which is an implied term in every lease that guarantees the tenant will have quiet and peaceful possession of the leased premises.
There are several ways a tenant’s right to quiet enjoyment can be violated. Some common examples of violations include:
- Entering the tenant’s premises without providing adequate notice
- Allowing too much noise that interferes with the tenant’s enjoyment of the premises
- Not taking the necessary precautions to keep the premises safe
- Allowing the tenant to be harassed by other tenants
- Locking out the tenant from the premises
A landlord would be in violation of the covenant of quiet enjoyment if they continuously allow a tenant to yell racial slurs at another tenant.
Consequences for Landlords Who Violate the Covenant of Quiet Enjoyment
There are different recourse options that tenants can take when their rights are violated, including but not limited to:
- Refusing to pay rent
- Bringing legal action
- Terminating the lease
Any of these actions would have a negative impact on the landlord. The landlord could also be liable for compensation such as moving expenses, attorney’s fees and other expenses.
When Can a Landlord Violate the Covenant of Quiet Enjoyment?
In Washington, a landlord cannot violate the covenant of quiet enjoyment under any circumstances.
However, actions that seem to violate the covenant of quiet enjoyment may be legal in certain circumstances. For example, a landlord may enter the premises without providing notice to the tenant, in the event of an emergency.
A landlord enters into a tenant’s premises because there is evidence of a flood.
7. Violate the Warranty of Habitability
In Washington, landlords must uphold the implied warranty of habitability, which is guaranteed in leases and ensures that the leased premises meet habitability requirements.
There are several ways a landlord may violate the warranty of habitability. Some common examples of violations include:
- Broken locks
- Lack of proper plumbing
- Lack of utilities such as heat, electricity and water
- Failure to exterminate a rodent infestation
A landlord violates the warranty of habitability, if, after notice of breaking, they do not repair the heating system in the winter.
Consequences for Landlords Who Violate the Warranty of Habitability
When a landlord violates the warranty of habitability, a tenant is entitled to relief such as:
- A court order directing the landlord to repair the condition
- A court order reducing the tenant’s rent
- A judgment for one months’ rent plus $500
- A judgment for actual damages
- Any court and attorneys’ fees
When Can a Landlord Violate the Warranty of Habitability?
Landlords in Washington cannot violate the warranty of habitability at any time.
8. Commit Constructive Eviction
A landlord in Washington cannot constructively evict tenants from the leased premises.
Constructive eviction is a circumstance where a tenant’s use of the property is so significantly impeded by actions under the landlord’s authority that the tenant has no alternative but to vacate the premises.
Examples of constructive eviction include:
- Failure to provide heating
- Failure to rid of a pest infestation
- Making the property uninhabitable
- Violating the quiet enjoyment of tenants
Consequences for Landlords Who Constructively Evict Tenants
Landlords who evict their tenants without just cause will be liable to the tenant for certain damages. If a court finds the landlord evicted the tenant without cause, the landlord may be liable for:
- One months’ rent plus $500
- Reasonable costs to move to another place
- Attorney’s fees and costs
- Injunctive relief
Once a court finds there was no cause for eviction, tenants will be allowed to return to the leased premises.
When Can a Landlord Constructively Evict a Tenant?
In Washington, a landlord cannot withhold services or force out a tenant so as to constructively evict them.
Although, if a tenant has violated the lease terms, then the landlord can perform actions that are generally associated with constructive eviction. After lease termination, landlords are not contractually obligated to provide the mandatory services outlined in the lease.
9. Defraud Tenants
When landlords communicate with tenants, they cannot make any statements under false pretenses, which may lead the tenant to believe something that is not true.
There are many ways in which a landlord can commit fraud, including:
- Making a false or misleading oral or written statement
- Representing that the property has a characteristic or use that it does not have
- Representing that the property is of a particular standard, quality, or style that it is not
- Failing to state a material fact if the failure deceives or tends to deceive
- Putting a clause in a lease that waives the tenant’s right to use a legal defense.
A landlord may not notify a prospective tenant that the rental premises are safe, while being aware the locks are broken and there have been recent break-ins.
Consequences for Landlords Who Defraud Tenants
Landlords who defraud current and prospective tenants may face litigation. Depending on the court, the tenant may be entitled to:
- Economic damages
- Statutory fraud damages
- Exemplary damages
- Mental anguish damages
- Attorney’s fees
- Equitable relief
- Declaratory judgment
When Can a Landlord Defraud Tenants?
In Washington, landlords cannot defraud tenants under any circumstance.
10. Fail to Pass State Inspections
Prior to renting out leased premises, landlords must register the rental premises with the proper authorities. Landlords must then conduct a proper inspection so that the premises are in a habitable condition for the tenant.
Consequences for Landlords Failing to Pass State Inspections
Failure to register the premises and conduct an inspection may lead to fines and other taxes.
When Can a Landlord Fail to Pass State Inspections?
Landlords must always pass state inspections to lease out the rental property.
Can a Landlord Deny Sublessees or Assignees?
Unless prior written consent has already been granted, a landlord can prohibit a tenant from subletting in Washington. A landlord reserves the right to deny any and all future requests from a tenant to sublease. However, a landlord cannot deny a qualified sublessee or assignee.
A qualified sublessee or assignee is one that:
- Has the financial ability to continue paying the rent
- Passes the background check
- Is a high character individual who will not cause the landlord trouble
Consequences for Landlords Who Deny Qualified Sublessees or Assignees
When a landlord denies a qualified subtenant or assignee, the original tenant may sue the landlord for damages. A tenant may be able to recover money equivalent to the amount of monthly rent for which the landlord disallowed the prospective subtenant or assignee from making payments.
Furthermore, damages associated with the landlord’s failure to mitigate damages may be possible. The duty to mitigate damages exists where the landlord must take reasonable steps to re-rent the unit to a replacement tenant.
When Can a Landlord Deny a Sublessee or Assignee?
A landlord can deny a sublessee when:
- The landlord has a good faith belief that the new tenant would not meet the financial obligations under the lease
- There needs to be an alteration to the premises for the use of the new tenant
- There would be an increase in the number of persons residing in the dwelling
- The landlord has a good faith belief of the new tenant’s inappropriate conduct
- The new tenant refuses to sign and comply with the lease
Can a Landlord Charge Unlimited Amounts for the Security Deposit?
In Washington, a landlord can charge an unlimited amount for the security deposit. There are no rent control laws capping the security deposit amount. However, landlords are expected to charge only a reasonable amount for the security deposit.
Generally, a reasonable amount for a Washington security deposit could be two times the amount of rent. So, if the monthly rent is $1,000, a landlord could require the tenant to pay $2,000 as a security deposit.
Can a Landlord Deduct Expenses From the Security Deposit?
Landlords in Washington can deduct expenses from the security deposit.
A landlord will be able to withhold a tenant’s security deposit for certain reasons. These reasons include:
- Any costs associated with damages incurred because of lease breaches
- Any costs associated with property damages not normal wear and tear
- Unpaid monthly rent
- Unpaid utilities
- Cleaning fees at the end of the lease
- Expenses incurred in securing a new tenant
- Whatever cancellation fee the lease may be provided for
Can a Landlord Sue a Tenant for Lease Violations?
In Washington, a landlord can sue a tenant for violating the lease. Common lease violations include:
- Illegal activity
- Unauthorized pets
- Disturbing other tenants
- Not keeping the premises clean
Landlords can recover damages such as unpaid rent, costs of property damage the tenant caused and eviction of the tenant.
Can a Landlord Enter into a Tenant’s Premises During an Emergency?
A landlord can enter into a tenant’s premises when there is an emergency.
In most cases, a landlord must give at least two days of advance notice before entering. This is reduced to one day for showing a property to potential tenants or buyers.
In the event of an emergency, such as a fire, burst water pipe, or gas leak, landlords have the right to enter without notice. They may also enter the premises if a tenant has moved out without notification, or if the landlord has a court order to do so.
Can a Landlord Conduct a Background Check on Prospective Tenants?
A landlord in Washington can conduct a background check on prospective tenants. In Washington, landlords must make available to the applicant, printed notice of the landlord’s tenant selection criteria, including:
- Criminal history
- Previous rental history
- Current income
- Credit history
In Washington, there are usually costs associated with background checks.
Can a Landlord Charge Late Fees for Late Rent?
In Washington, a landlord can charge late fees for late rent. According to statute, a landlord can charge up to a certain percentage of the monthly rent as a late penalty. If the landlord is going to charge a late fee, the following requirements need to be met:
- Notice of the fee is included in the written lease
- The fee is reasonable
Can a Landlord Set Occupancy Limits?
Washington law requires that landlords set occupancy limits depending on the type of property the landlord owns.
Generally, the maximum number of adults that a landlord may allow to occupy a dwelling is three times the number of bedrooms in the premises. There are certain exceptions allowing a higher occupancy limit such as state or federal laws that allow a higher occupancy rate or if an adult is seeking temporary sanctuary from family violence.
Can a Landlord Require Certain Forms of Payment?
A landlord in Washington can require certain forms of payment, but only a personal check, cashier’s check, or money order. Landlords must accept these forms of payment, and cannot require payment in cash or payment by electronic form.
A landlord does not have to accept cash as rent payment, but when taking cash, must provide a written receipt confirming payment.
Can a Landlord Charge an Application Fee?
In Washington, a landlord can charge an application fee associated with a rental application. The fee is to pay the landlord’s cost of running a background check on a prospective tenant.
If the landlord rejects an applicant and the landlord has not made proper notice, the landlord will have to return the application fee. Furthermore, if an applicant requests a landlord to mail a refund of the applicant’s application fee to the applicant, the landlord shall mail the refund check to the applicant.
Sources
- 1 WA Rev Code § 59.18.240
-
The landlord shall not take or threaten to take reprisals or retaliatory action against the tenant because of any good faith and lawful
Source Link - 2 HUD Complaint and Investigation Process
-
If neither party elects to have a federal civil trial before the 20-day Election Period expires, HUD will promptly schedule a hearing for your case before an ALJ…payment of damages.
Source Link - 3 WA Rev Code §49.60.222
-
Nothing in (a) or (b) of this subsection shall apply to: (i) A single-family house rented or leased by the owner if the owner does not own or have an interest in the proceeds of the rental or lease of more than three such single-family houses at one time, the rental or lease occurred without the use of a salesperson, or a broker as defined in RCW 18.85.011,
Source Link - 4 WA Rev Code §59.18.190
-
Whenever the landlord learns of a breach of RCW 59.18.130 or has accepted performance by the tenant which is at variance with the terms of the rental agreement or rules enforceable after the commencement of the tenancy, he or she may immediately give notice to the tenant to remedy the nonconformance. Said notice shall expire after sixty days unless the landlord pursues any remedy under this chapter.
Source Link - 5 Sherwood Auburn LLC v. Pinzon, 521 P.3d 212, 220 (Wash. Ct. App. 2022)
-
…the plain language of the CARES Act notice provision requires that landlords subject to the act provide a 30-day notice to tenants prior to commencing an unlawful detainer action.
Source Link - 6 KHCA v. Knight, No. 85031-8-I, at 18 (Wash. Ct. App. Feb. 26, 2024)
-
…the plain meaning of Section 4024’s 30-day notice to vacate provision is that it applies only to evictions stemming from nonpayment of rent.
Source Link - 7 Pendleton Place, LLC, v. Asentista, No. 58118-3-II (Wash. Ct. App. Jan. 9, 2024)
-
…we conclude that the 30-day notice provision in 15 U.S.C. § 9058(c)(1) applies to all evictions of tenants living in covered dwelling units, not just those for nonpayment of rent.
Source Link - 8 WA Rev Code § 35.21.830
-
No city or town of any class may enact, maintain, or enforce ordinances or other provisions which regulate the amount of rent to be charged for single-family or multiple-unit residential rental structures or sites other than properties in public ownership, under public management, or properties providing low-income rental housing under joint public-private agreements for the financing or provision of such low-income rental housing.
Source Link - 9 WA Rev Code §59.18.253
-
A landlord who charges a prospective tenant a fee or deposit to hold a dwelling unit or secure that the prospective tenant will move into a dwelling unit, after the dwelling unit has been offered to the prospective tenant, must provide the prospective tenant with a receipt for the fee or deposit, together with a written statement of the conditions, if any, under which the fee or deposit may be retained, immediately upon payment of the fee or deposit.
Source Link - 10 Wash. Rev. Code. § 59.18.030
-
“Wear resulting from ordinary use of the premises” means deterioration that results from the intended use of a dwelling unit, including breakage or malfunction due to age or deteriorated condition. Such wear does not include deterioration that results from negligence, carelessness, accident, or abuse of the premises, fixtures, equipment, appliances, or furnishings by the tenant, immediate family member, occupant, or guest.
Source Link - 11 Wash. Rev. Code § 59.18.280(1)(c)
-
No portion of any deposit may be withheld:
(i) For wear resulting from ordinary use of the premises;
(ii) For carpet cleaning unless the landlord documents wear to the carpet that is beyond wear resulting from ordinary use of the premises;
(iii) For the costs of repair and replacement of fixtures, equipment, appliances, and furnishings if their condition was not reasonably documented in the written checklist required under RCW 59.18.260; or
(iv) In excess of the cost of repair or replacement of the damaged portion in situations in which the premises, including fixtures, equipment, appliances, and furnishings, are damaged in excess of wear resulting from ordinary use of the premises but the damage does not encompass the item’s entirety.
Source Link - 12 Wash. Rev. Code § 59.18.280(1)(b)
-
With the statement required by (a) of this subsection, the landlord shall include copies of estimates received or invoices paid to reasonably substantiate damage charges. Where repairs are performed by the landlord or the landlord’s employee, if a deduction is made for materials or supplies, the landlord shall provide a copy of the bill, invoice, or receipt. The landlord may document the cost of materials or supplies already in the landlord’s possession or purchased on an ongoing basis by providing a copy of a bill, invoice, receipt, vendor price list, or other vendor document that reasonably documents the cost of the item used in the repair or cleaning of the unit. Where repairs are performed by the landlord or the landlord’s employee, the landlord shall include a statement of the time spent performing repairs and the reasonable hourly rate charged.
Source Link - 13 Wash. Rev. Code § 59.18.280(2)
-
If the landlord fails to give the statement and any documentation required by subsection (1) of this section together with any refund due the tenant within the time limits specified in subsection (1) of this section he or she shall be liable to the tenant for the full amount of the deposit. The landlord is also barred in any action brought by the tenant to recover the deposit from asserting any claim or raising any defense for retaining any of the deposit unless the landlord shows that circumstances beyond the landlord’s control prevented the landlord from providing the statement and any documentation within the 30 days or that the tenant abandoned the premises as defined in RCW 59.18.310. The court may in its discretion award up to two times the amount of the deposit for the intentional refusal of the landlord to give the statement, documentation, or refund due unless the landlord shows that circumstances beyond the landlord’s control prevented the landlord from providing the statement and any such documentation within 30 days or that the tenant abandoned the premises as described in RCW 59.18.310. In any action brought by the tenant to recover the deposit, the prevailing party shall additionally be entitled to the cost of suit or arbitration including a reasonable attorneys’ fee.
Source Link - 14 WA Rev Code §59.18.060
-
The landlord will at all times during the tenancy keep the premises fit for human habitation, and shall in particular maintain the premises to substantially comply with any applicable code, statute, ordinance, or regulation governing their maintenance or operation
Source Link - 15 WA Rev Code §59.18.060
-
Local municipalities may require that landlords provide a certificate of inspection as a business license condition. A local municipality does not need to have a business license or registration program in order to require that landlords provide a certificate of inspection. A certificate of inspection does not preclude or limit inspections conducted pursuant to the tenant remedy as provided for in RCW 59.18.115, at the request or consent of the tenant, or pursuant to a warrant.
Source Link - 16 Wash. Rev. Code § 59.18.150(6)
-
The landlord shall not abuse the right of access or use it to harass the tenant, and shall provide notice before entry as provided in this subsection. Except in the case of emergency or if it is impracticable to do so, the landlord shall give the tenant at least two days’ written notice of his or her intent to enter and shall enter only at reasonable times. The notice must state the exact time and date or dates of entry or specify a period of time during that date or dates in which the entry will occur, in which case the notice must specify the earliest and latest possible times of entry. The notice must also specify the telephone number to which the tenant may communicate any objection or request to reschedule the entry. The tenant shall not unreasonably withhold consent to the landlord to enter the dwelling unit at a specified time where the landlord has given at least one day’s notice of intent to enter to exhibit the dwelling unit to prospective or actual purchasers or tenants. A landlord shall not unreasonably interfere with a tenant’s enjoyment of the rented dwelling unit by excessively exhibiting the dwelling unit.
Source Link - 17 WA Rev Code §19.150.150
-
No late fee shall be collected unless it is written in the rental agreement or as an addendum to such agreement. An owner may impose a reasonable late fee for each month an occupant does not pay rent when due. A late fee of twenty dollars or twenty percent of the monthly rental amount, whichever is greater, for each late rental payment shall be deemed reasonable, and shall not constitute a penalty.
Source Link - 18 Wash. Rev. Code § 59.18.063
-
(1) A landlord must accept a personal check, cashier’s check, or money order for any payment of rent made by a tenant, except that a landlord is not required to accept a personal check from any tenant that has had a personal check written to the landlord or the landlord’s agent that has been returned for nonsufficient funds or account closure within the previous nine months. A landlord must also allow for the tenant to submit a rental payment by mail unless the landlord provides an accessible, on-site location.
(2) A landlord may refuse to accept cash for any payment of rent made by a tenant, but shall provide a receipt for any payment made by a tenant in the form of cash when the landlord accepts cash.
(3) A landlord shall provide, upon the request of a tenant, a written receipt for any payments made by the tenant in a form other than cash.
Source Link