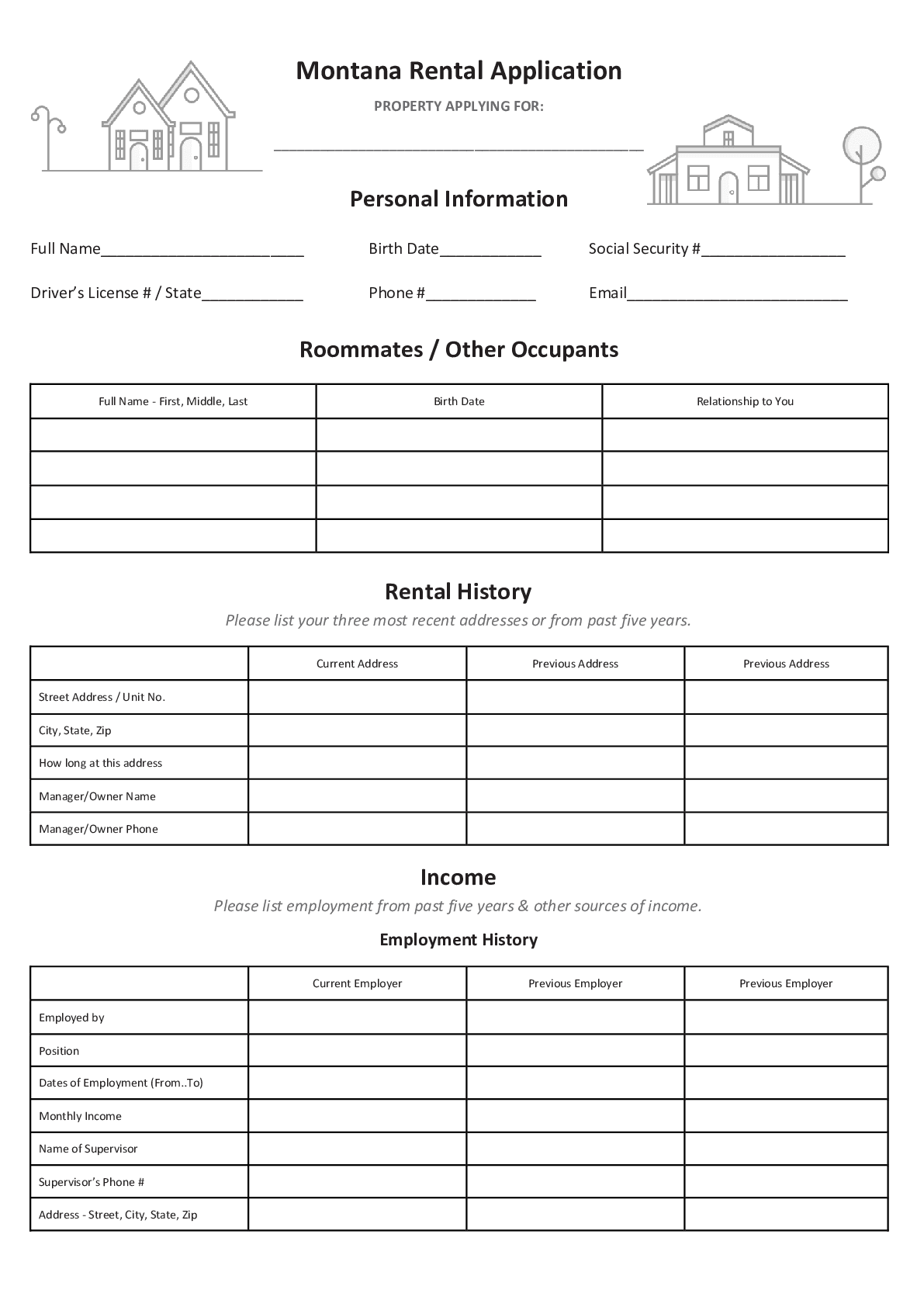
A Montana rental agreement is a legal contract between a landlord overseeing a rental property and a tenant using the property. Delaware landlord-tenant law governs and regulates these agreements.
Montana Rental Agreement Types
A Montana roommate agreement is a legal contract between two or more people (“co-tenants”) who share a rental property according to rules they set, including for things like splitting the rent. This agreement binds the co-tenants living together, and doesn’t include the landlord.
Montana Required Lease Disclosures
- Landlord’s Name and Address (required for all leases) – Montana leases must contain landlord’s name and address, or that of their authorized agent. This allows required communication (for example, about repairs) to happen in a smooth way. Typically includes additional contact information, such as phone numbers and email addresses.
- Move-In Checklist (required for some leases) – Montana landlords may only charge a security deposit if they include a move-in checklist itemizing any existing property damage. This ensures accurate deductions when the tenant moves out.
- Mold Disclosure (required for some leases) – Montana leases must provide a statutory disclosure for any property with mold contamination.
- Methamphetamine Contamination Disclosure (required for some leases) – Montana leases must disclose any known contamination the manufacture or use of methamphetamine on the rental property.
- Lead-Based Paint Disclosure (required for some leases) – Landlords must provide an EPA-approved disclosure and informational pamphlet to tenants renting any property built before 1978.
To learn more about required disclosures in Montana, click here.
Montana Landlord Tenant Laws
- Warranty of Habitability – Montana landlords can only rent out habitable property. This means providing certain basic health and safety features like heat, plumbing, and electricity. Landlords must repair any issues within 14 days after proper notice (3 days, for emergency issues). Failure to repair lets a tenant sue the landlord, end the lease, or repair and deduct from the rent. Tenants usually aren’t allowed to withhold rent.
- Evictions – Montana landlords may evict for rent default, lease violations, or illegal acts, among other things. Before filing eviction, landlords must serve tenants with prior notice to pay, comply or quit, depending on the eviction type. This means most evictions in Montana take between a few days to a few weeks.
- Security Deposits – Montana does not limit the amount of a security deposit. When a lease ends, a landlord has 10 days to return any unused portion of a tenant’s deposit.
- Lease Termination – Montana allows month-to-month tenants to end a lease with 30 days of advance notice. Terminating a fixed-term lease usually requires active military duty, landlord harassment, uninhabitable property, or domestic abuse.
- Rent Increases and Fees – Montana does not limit the amount of a rent increase. Landlords must provide at least 15 days of advance notice before increasing the rent. Late fees have no limit (so, as agreed by the lease). Bounced check fees are limited to $30 per instance.
- Landlord Entry – Montana landlords may enter rental property for reasonable business purposes, like maintenance, inspections, and showings. Unless it’s an emergency, they must provide at least 24 hours of advance notice.
- Settling Legal Disputes – Montana lets small claims court decide landlord-tenant issues, including evictions, as long as the amount in controversy is under $7,000. Most landlord-tenant disputes fall under the 5-year statute of limitations for contracts (3 years, for oral contracts).
To learn more about landlord tenant laws in Montana, click here.
Sources
- 1 Mont. Code Ann. § 27-1-717(2)
-
The person who issues the [dishonored] check, draft, converted check, electronic funds transfer, or order is liable to the payee or the payee’s assignee for a service charge in an amount not greater than $30.
Source Link